Table
1:
The
equation of time correction-table
 The
equation of time refers to the irregularity of the
natural length of a day as measured on a sundial. This
irregularity is caused by the non-circular orbit of the
earth spinning around the sun and the tilt of its axis
relative to the sun. Combined it gives the composite
curve as presented below. In the form of a correction
table is the graph below presented in the form of the
Full
Calendar of Order.
With this table one can set a reference clock to the sun.
For its practical use day by day with the help of the
internet is provided the Tempometer:
a PHP- page that, given one's longitude, automatically
calculates the true position of the sun and displays it
in the form of normal clocktime. Twelve o'clock on the
tempometer means that the sun at that time passes the
meridian, goes through the south, passes the longitude of
the place of the user. The graph below shows the
difference the sundial makes with the mean local time of
a clock. A
positive value means
the clock has to be set
back
so many minutes departing from mean local time in order
to read the true of solar time. The curve of this table
looks as follows:
The
equation of time refers to the irregularity of the
natural length of a day as measured on a sundial. This
irregularity is caused by the non-circular orbit of the
earth spinning around the sun and the tilt of its axis
relative to the sun. Combined it gives the composite
curve as presented below. In the form of a correction
table is the graph below presented in the form of the
Full
Calendar of Order.
With this table one can set a reference clock to the sun.
For its practical use day by day with the help of the
internet is provided the Tempometer:
a PHP- page that, given one's longitude, automatically
calculates the true position of the sun and displays it
in the form of normal clocktime. Twelve o'clock on the
tempometer means that the sun at that time passes the
meridian, goes through the south, passes the longitude of
the place of the user. The graph below shows the
difference the sundial makes with the mean local time of
a clock. A
positive value means
the clock has to be set
back
so many minutes departing from mean local time in order
to read the true of solar time. The curve of this table
looks as follows:

The
equation of time graphically (source)
Mean
(local) time is derived by multiplying one's longitude
(see any map or atlas or use this search engine) with 4
adding it up to GMT Worldtime.
So for
instance at longitude 30 East from Greenwich one is 4
times 30 = 120 minutes (two hours) later than Greenwich
Worldtime of GMT, Greenwich Mean or local Time
(UTC,
also called Universal
Time).
UTC:
West of
Greenwich gives the number of minutes earlier than UTC.
To have the exact of true time one, as said, then has to
add or subtract the minutes according
the table of the Full Calendar of
Order.
Positive values must be subtracted, negative values
added. (know also your local
zone-time
and the timezone
table of the Greenwich
2000-site
, or
click here to see a map
and/or an update).
One's calculations are proper when 12 o'clock true time
shows the noonshadow of the sun exactly north/south. (in
other words accords with the 12 hour-indication on a
sundial). There is a calculation-helper
to set a clock to the sun quickly.
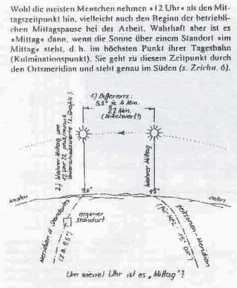
The
sun passing the meridian is in the south
The
meaning of the colors of the table contained in the Full
Calendar of order:
-
The white
and
pink
fields
constitute the division of the Cakra
calendar
that serves as a calendar reference of the natural
solar order to the cultural timeconsciousness of 7-day
weeks on a normal civil calendar
-The
beige
fields
are the normal Cakra weekdays (note that this calendar
does not show the 7-days- regular division of a normal
calendar).
-
The red
fields
constitute the lunar calendar with at the bottom the
old roman numerals for the original count of the
months. K
means Kalends and is the new moon.
N
means Nones and is in this concept either the first or
the last quarter originally the romans didn't count
the second quarter). The I
means
Ides and indicates the full moon.
-
The two yellow
and ochre
fields indicate the dates on which the Galactic old
and new years day take place of having earth the
closest to the centre of the galaxy (see
The
Galactic Order).
Below
the table of this Full Calendar of Order there are
suggestions given for the use of this composite
calendar.
N.B.
The table has a shift of phase in the equation of time of
1 day in 25 years.
*:
Leaping is for the Cakra calendar done the 21 of
dec. so that in a leapyear all indications of the
cakracalendar shift for one day after this
day.





